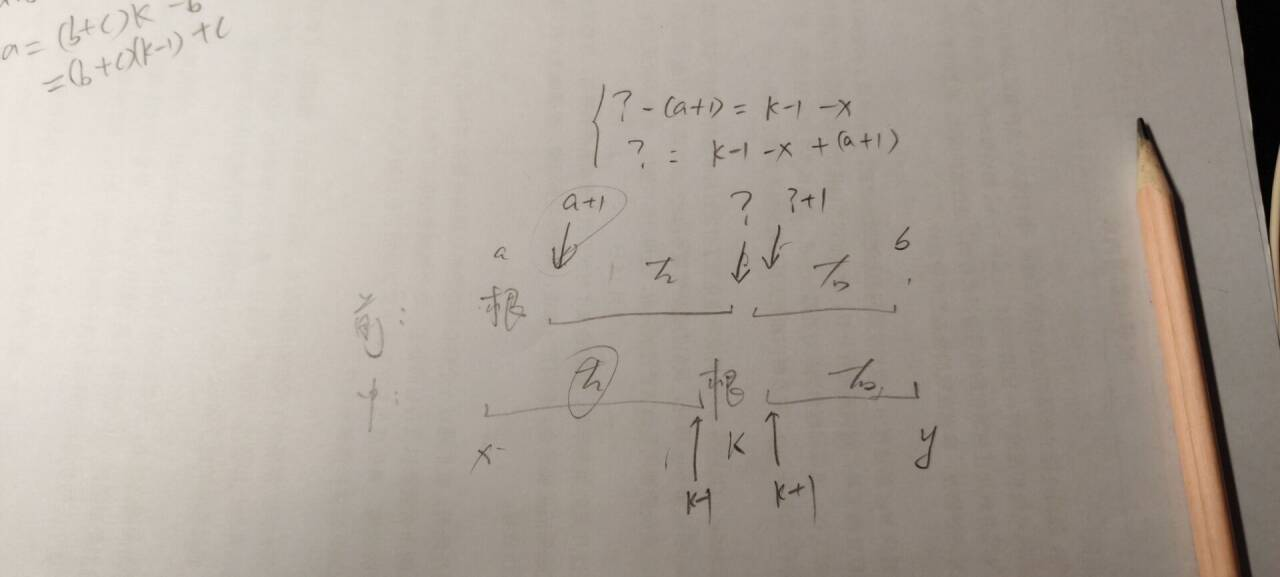mirror of
https://github.com/CaiJimmy/hugo-theme-stack.git
synced 2025-07-13 08:13:31 +08:00
35 KiB
35 KiB
+++ author = "Wxn" title = "给个offer" date = "2024-04-24" description = "Please read me first." tags = [ "Dilay", ] categories = [ "面试复盘", ]
+++
This article offers a sample of basic Markdown.
正文开始
如果考到数论的题,会做你就做,不会做你就说你对数论这块不太熟悉,数论这个面算法工程师考的比较多,做开发的话链表比较多
1.41. 包含min函数的栈
//https://leetcode.cn/problems/bao-han-minhan-shu-de-zhan-lcof/description/
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
//1.单调栈
//2.主栈与辅助栈
//3.1)push都要插入(如果辅助栈为空,或者辅助栈顶>=x,则辅助栈插入)
//2)pop() 如果辅助栈顶 == 主栈顶,则辅助栈顶弹出,否者就只有主栈弹出
//3)4)直接返回相应的栈
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
}
void pop() {
}
int top() {
}
int getMin() {
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
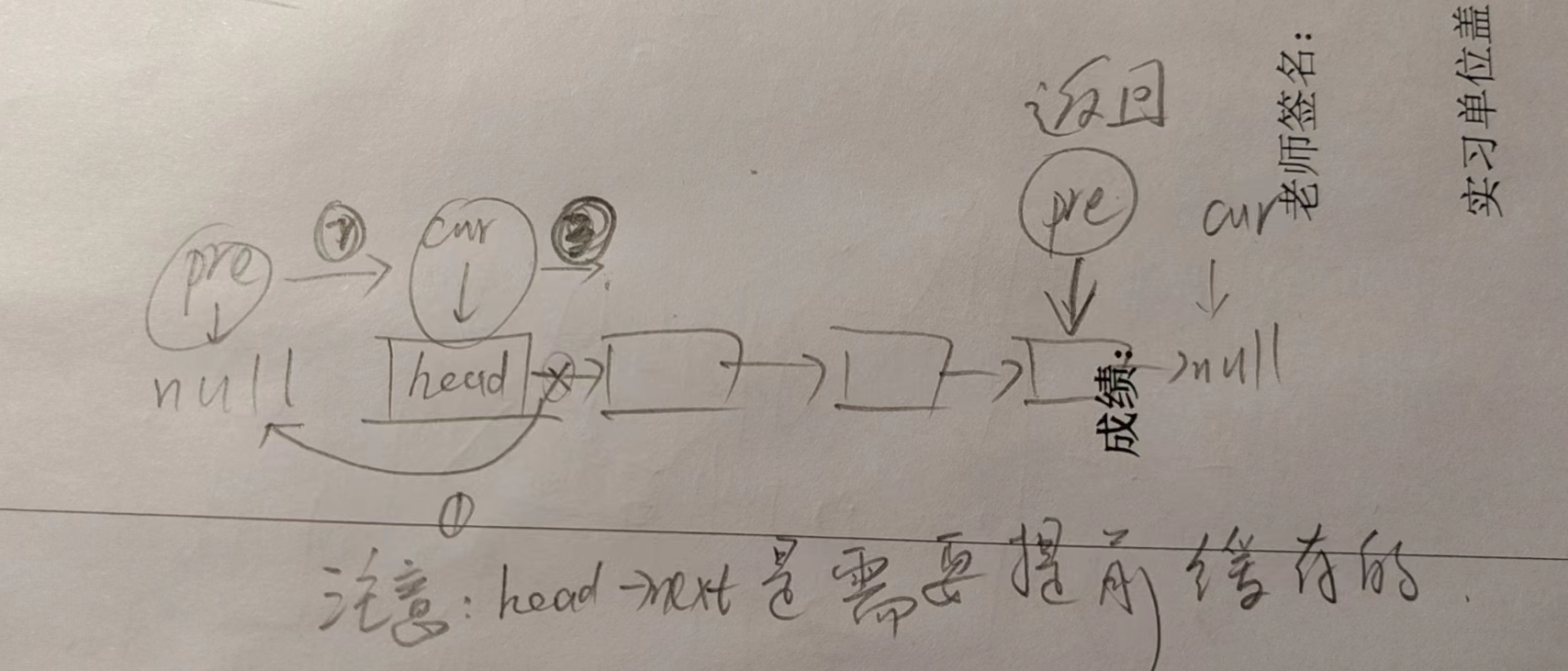
2.35. 反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
//难点:单链表要建立一个前驱节点
//关键点:画图
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
}
};
3.19. 二叉树的下一个节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode *father;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), father(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//这个是vip题目
//285. 二叉搜索树中的中序后继
//分类讨论:有右子树和没有右子树
//中序遍历
//情况1:这个点有右子树,那后继就是"右子树"最左边的那个
//情况2:这个点的右子树为空(且有父节点),当p有父节点且p等于p父节点的右儿子,那么p就赋值为p的父节点,最后返回p的父节点
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* inorderSuccessor(TreeNode* p) {
}
};
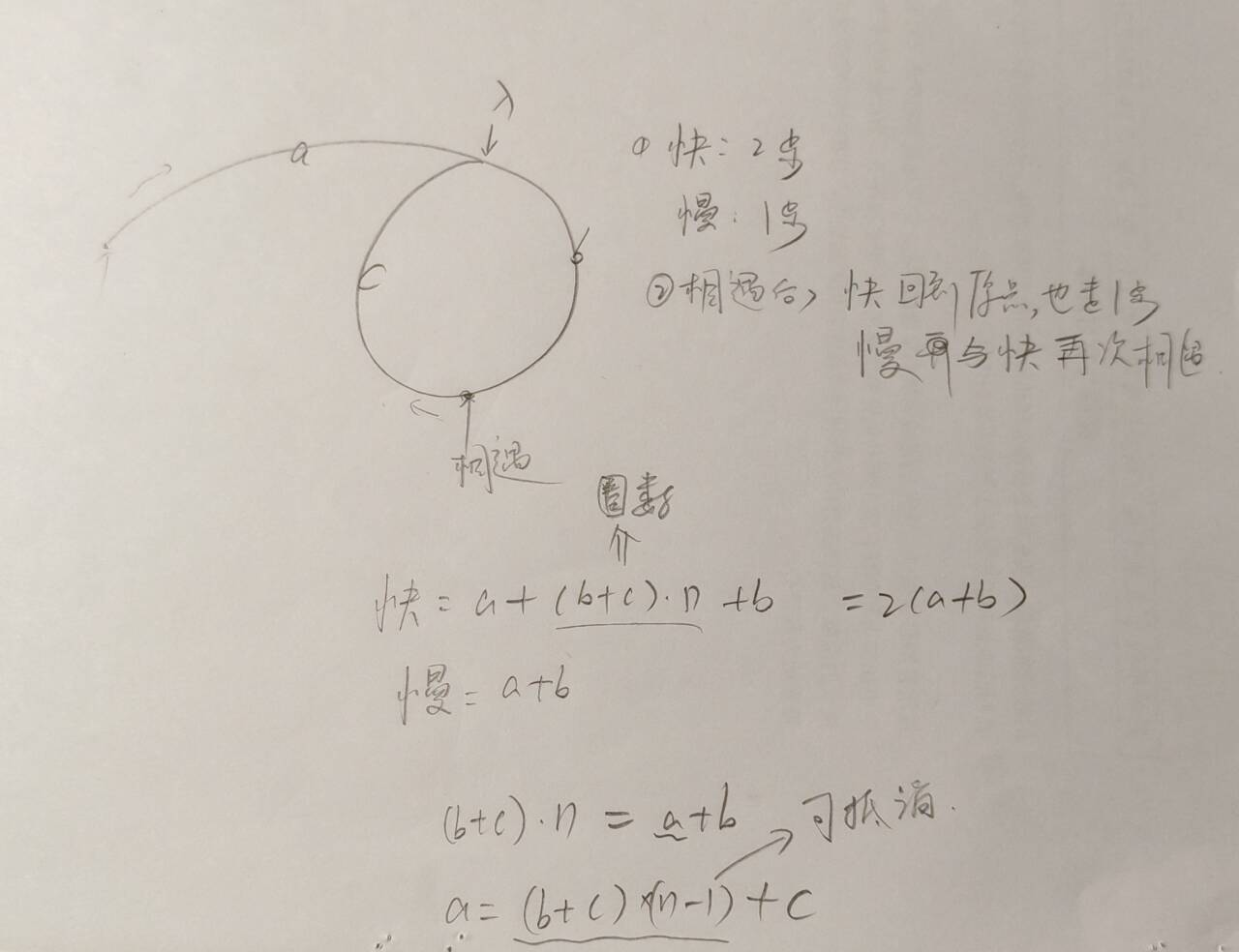
4.34. 链表中环的入口结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
}
};
画图:数学证明:(b+c)表示n圈
备份
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode *head) {
auto first = head,slow = head;
while(first && first->next && first->next->next)
{
first = first->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(first == slow)
{
first = head;
while(first != slow)
{
first = first->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return first;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
5.77.翻转单词顺序
//先翻转整个句子
//再翻转单独的一个单词
//难点:在找到一段时,不要忘记边界
void Reverse(int l ,int r,string& s)
{
for(int i = l , j = r ;i < j ;i++,j--)swap(s[i],s[j]);
}
Reverse(0,s.size()-1,s);
等价于
reverse(s.begin()+0,s.begin()+s.size());//范围:[)
反转不是空格的那一段
6.18.重建二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//前:根左右
//中:左根右
//1.使用哈希表,快速的找到"一个元素在中序遍历的位置"
//2.递归dfs(主函数直接返回)
//1)递归参数:左右子树节点个数
//2)递归内部:
/*
- 前序遍历:左>右 -> null
- 根节点的值为前序遍历的第1个点 preorder[a]
- 找到根节点在哈希表中的位置
- 左右子树递归创建 范围画图
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
}
};
7.21. 斐波那契数列
//f[i] = f[i-1]+f[i-2]
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
}
};
8.78. 左旋转字符串
//先把整个进行翻转
//再把前(总-个数),后两部分进行翻转
class Solution {
public:
string leftRotateString(string str, int n) {
}
};
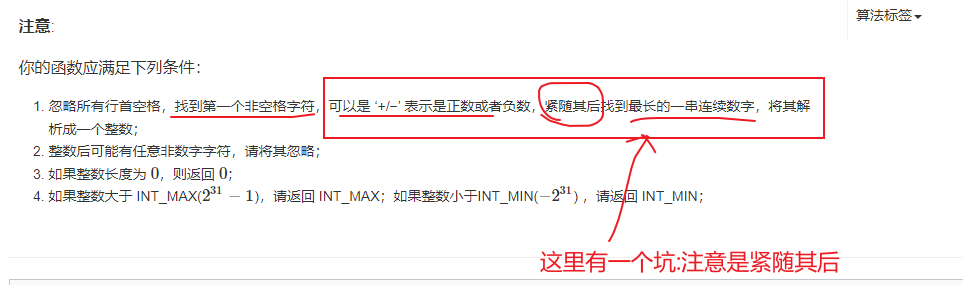
9.87. 把字符串转换成整数
//分步
//过滤掉行首空格
//long long
//判断这个数是不是负数
//如果在累加的过程中(还没加完),就已经越界了,那就直接跳出来
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
}
};
10.28. 在O(1)时间删除链表结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//1.用下一个节点覆盖掉当前节点
//2.删除掉当前节点
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
}
};
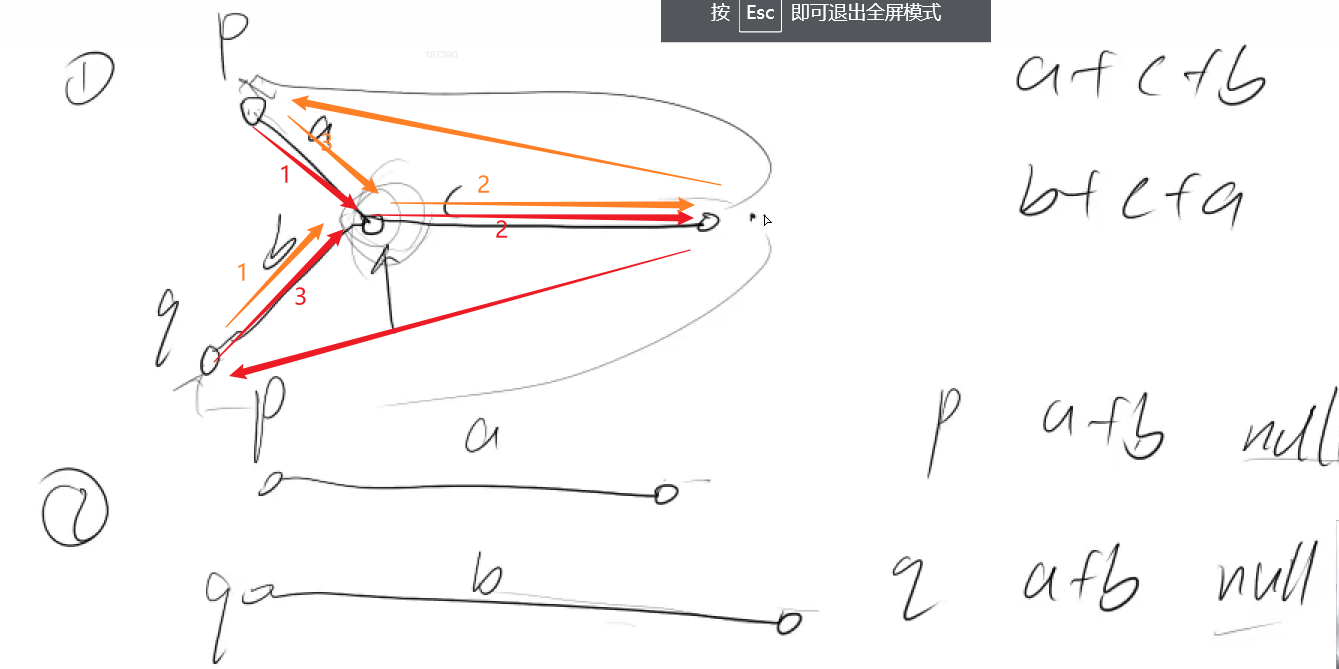
11.66. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//双指针,
//指针1走完a再走b,指针2走完b再走a,返回最后相遇的位置,如果最后都指向空也算相遇了
//这个也是有难点的: 注意:对于指针1与指针2,要么是"回头",要么是"下一个"
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
}
};
12.84. 求1+2+…+n
//语法题:(false && 条件); = false 可以起到if的效果
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(int n) {
}
};
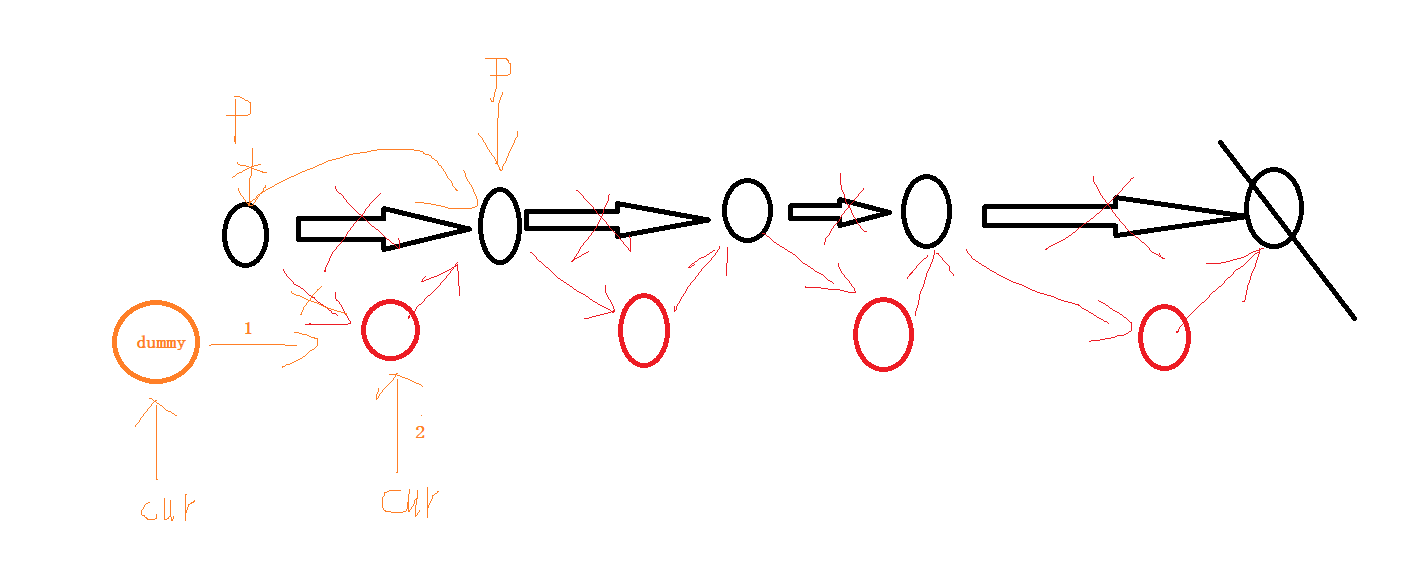
13.36. 合并两个排序的链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//归并排序(一个函数足够)
//虚拟节点(比如说初始化为-1)+当前节点
//1)两个指针
//2)比较两个指针的值哪个小,哪个小就给哪个(如果l1)
//3)链到虚拟链表,当前节点后移,l1也后移
//4)处理残局:l1与l2哪个不同,就一直链到空为止
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
}
};
14.14. 不修改数组找出重复的数字
//简单方法:哈希表
//方二:抽屉原理
//二分法:
//一个萝卜一个坑,假如说数的个数>坑的个数,那么这个区间一定存在重复的数
//注意:给定一个长度为 n+1的数组nums,数组中所有的数均在 1∼n的范围内,其中 n≥1,表示下标有效的范围是[1,nums.size()-1]
class Solution {
public:
int duplicateInArray(vector<int>& nums) {
// l 和 r 分别代表的是 数字 1 和 数字n 这里并不是下标.
int l = 1, r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l < r){
// 二分 找到中间的那个数
int mid = l + r >> 1;
int s = 0;
// 下面这句话的意思 从 nums里面 循环去先去 判断 这个数 x 的值看他是否在 [l, mid]中间, 在的话 判断条件执行完为true
// true 的话代表 数字 1 flase 代表 数字 0. 然后再进行累加 s += x 统计符合条件的个数.
// 最终的效果就是 统计了 整个数组中 数的值 在 [l,mid] 之间的个数.
for (auto x : nums) s += x >= l && x <= mid; // left : [l, mid] , right : [mid + 1, r]
// 理解: 一个坑存一个数, 正常情况下 一定是坑的个数 和 数的个数相等. 如果一坑里面有两个数. 那么就会出现
// 数的个数 大于 坑的个数 说明 这个区间段一定存在重复的个数.
if (s > mid - l + 1) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;//l和r都可以
}
};
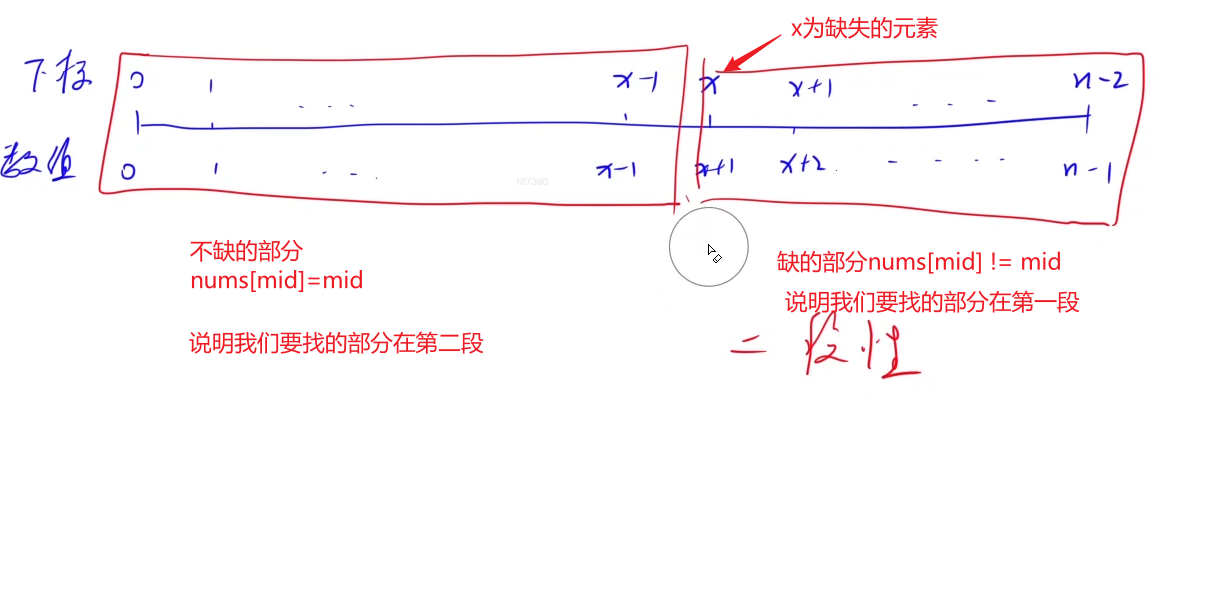
15.68. 0到n-1中缺失的数字
//二分
//通过下标直接查找,
//因为是连续的,如果不少的话,则有nums[mid] == mid,如果是左边少了,就是不等
//最后还要判断nums[r] == r,要是等于的话,那就是少最后一个
class Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
}
};
eg:
//[0,1,2,4] n=4
//[0,1,2,3] n=4
class Solution {
public:
int getMissingNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty())return 0;
int n = nums.size();
if(nums.back() == n-1)return n;//缺少最后面一个数
int l = 0 ,r = n-1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(nums[mid] == mid)l = mid +1;//这部分不缺
else r = mid;
}
return r;
}
};
补充:13. 找出数组中重复的数字
//哈希表秒了
//方二:不要了
class Solution {
public:
int duplicateInArray(vector<int>& nums) {
}
};
16.75. 和为S的两个数字
//时间复杂度最重要
//用法哈希表,count看是否存在
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findNumbersWithSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
}
};
17.23. 矩阵中的路径
//dfs
//枚举起点,枚举方向
//起点怎么枚举:两个for循环
//方向怎么枚举?上右下左:画图
//dfs中:
//1)刚好遍历到的字符个数u == 字符串的长度,就OK
//2)如果u下标字符 != 遍历到的字符,就不ok
//3)遍历四个方向,为了避免回头遍历,比如你刚遍历完一个字符'a',下一个字符还是'a',就会回头遍历,
//我们要避免这个,就需要先修改为一个其他的,等遍历完再返还
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string &str,int u ,int x,int y)
{
if(str[u] != matrix[x][y])return false;//当前字符与之不符
if(u == str.size()-1)return true;//刚好是最后一个,而且能来到这,说明相符
int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0},dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
char t = matrix[x][y];
matrix[x][y] = '*';
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ;i++)
{
int a= x+dx[i],b = y +dy[i];
if(a>=0 && a<matrix.size() &&b>=0 && b<matrix[a].size())
if(dfs(matrix,str,u+1,a,b))return true;
}
matrix[x][y] = t;
return false;
}
bool hasPath(vector<vector<char>>& matrix, string &str) {
for(int i = 0 ; i < matrix.size() ; i++)
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < matrix[i].size() ; j++)
{
if(dfs(matrix,str,0,i,j))
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
18.55. 连续子数组的最大和
s表示收益
res表示最终结果
19.42. 栈的压入、弹出序列
关键:不是所有的数都入栈,他才开始进行弹出操作.
完全可以实现这么一种情况:你还进去,人家就已经出来了
//1.长度不同,肯定不行
//2.用一个栈来模拟整个过程
//3.一直将pushV的元素入栈,直到栈顶元素 == 要弹出的第i元素(i从0开始)
//(while循环 --->尽可能的把能弹出的元素弹出来[前提:栈中有元素且栈顶元素刚好是我们要弹出的元素])
//4.最后如果栈为空,即为ok
class Solution {
public:
bool isPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
}
};
20.70. 二叉搜索树的第k个结点
//例子中:第1小的数是1;第二小数是2;第三小的数是3;
//所有:就是求中序遍历的第k个
//中序遍历:我们都知道是左根右,左和右就是一个dfs,那么中是难点
//中序遍历的中:k--,如果k==0,就是我们的答案
//最后dfs加一个阀门:如果节点指针为空,则直接return
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* kthNode(TreeNode* root, int k) {
}
};
21.48. 复杂链表的复刻
//1.给旧链表每2个节点之间加1个节点(新节点的值是前节点的值)
//2.重新遍历链表中的每个节点 (p->next)->random=(p->random)->next;
//3.将新链表拎出来:
//1)搞个虚拟头结点,最后返回dummy->next
//2)一有虚拟节点,那必须有一个cur节点
//3)画图:
// 1.cur->next = p->next;
// 2.cur = cur->next;
// 3.难点:需要把新旧链表彻底分开p->next = p->next->next;
// p = p->next;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next, *random;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *copyRandomList(ListNode *head) {
}
};
22.53. 最小的k个数
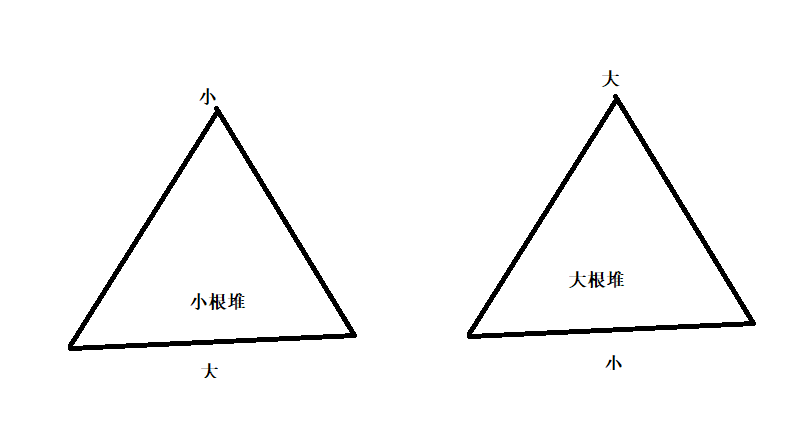
//使用大根堆priority_queue
//只放k个,多了就踢了
//最后记翻转
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
priority_queue<int>heap;
for(auto x : input)
{
heap.push(x);
if(heap.size() > k)heap.pop();//把堆顶删了
}
vector<int>res;
while(heap.size())
{
res.push_back(heap.top());
heap.pop();
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
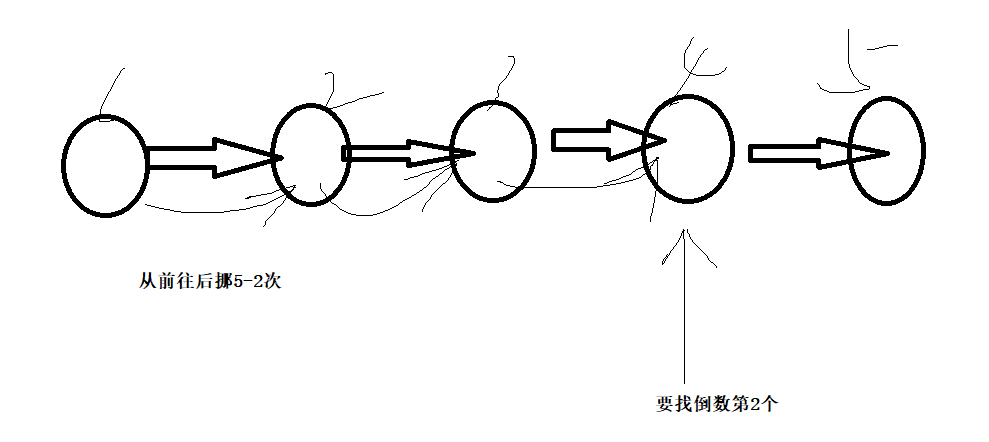
23.33. 链表中倒数第k个节点
//先求链表长度n
//链表中倒数第k个节点 == 链表从前往后挪n-k次
//简单画个图
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* findKthToTail(ListNode* pListHead, int k) {
}
};
24.71. 二叉树的深度
//max(左子树,右子树)+1
//dfs
//一共两行代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int treeDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return 0;
return max(treeDepth(root->left),treeDepth(root->right))+1;
}
};
25.72. 平衡二叉树
//这个题和求树的最大深度一样
/*
if(!root)return 0;
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
}
};
//错误的做法:只能保证根节点的左右子树,相差不超过1,不能拿保证"任意结点的左右子树的深度相差不超过 1"
// //树的深度
// class Solution {
// public:
// int dfs(TreeNode* root)
// {
// if(!root)return 0;
// return max(dfs(root->left),dfs(root->right))+1;
// }
// bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
// if(!root)return true;
// int l = dfs(root->left);
// int r = dfs(root->right);
// //cout<< l<<' '<<r<<' ';
// if(abs(l-r)>1)return false;
// return true;
// }
// };
//正确的:他计算了任意一个节点的左右子树的高度不超过1
class Solution {
public:
bool res = true;
int dfs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return 0;
int left = dfs(root->left) ,right = dfs(root->right);
if(abs(left-right)>1)res = false;
return max(left,right)+1;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
};
26.15. 二维数组中的查找
//每列是递增的
//难点:右上角
//(i,j)=>(0,array[0].size()-1)
//在范围内:(i<array.size() && j>=0)
//x = array[i][j],直接返回true
//x > target j--;
//else i++;
class Solution {
public:
bool searchArray(vector<vector<int>> array, int target) {
}
};
27.59. 把数字翻译成字符串
//dp的问题:直接记下来就行了
class Solution {
public:
int getTranslationCount(string s) {
int n = s.size();
vector<int> f(n + 1);//因为dp从1开始
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
f[i] = f[i - 1];//f[i]包含了f[i - 1]的所有情况
if (i > 1) {
int t = s[i - 1] - '0' + (s[i - 2] - '0') * 10;//状态转移的条件:只有[10,25]才可以状态转移
if (t >= 10 && t <= 25) f[i] += f[i - 2];//条件all满足:f[i] = f[i - 1]+f[i - 2];
}
}
return f[n];
}
};
29.37. 树的子结构
以根为开始,开始进行p1与p2的匹配:
需要另写一个函数进行匹配,函数的参数是以p1,p2为根节点的一段小树
函数内部实现:
1.p2为空.说明之前的匹配好了,直接return true;
2.p1为空 或者 p1和p2的值不匹配,直接return false;
3.没有被条件1和2直接return,说明当前的节点是匹配的,我们接着
匹配左左和右右,是且的关系
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* p1, TreeNode* p2)
{
if(!p2)return true;
if(!p1 || p1->val != p2->val)return false;
//此时,当前节点是匹配的
return dfs(p1->left,p2->left) && dfs(p1->right,p2->right);//左边匹配且右边匹配
}
bool hasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) {
if(!pRoot1 || !pRoot2)return false;
if(dfs(pRoot1,pRoot2))return true;//遍历当前节点
return hasSubtree(pRoot1->left,pRoot2) || hasSubtree(pRoot1->right,pRoot2);//下一个节点
}
};
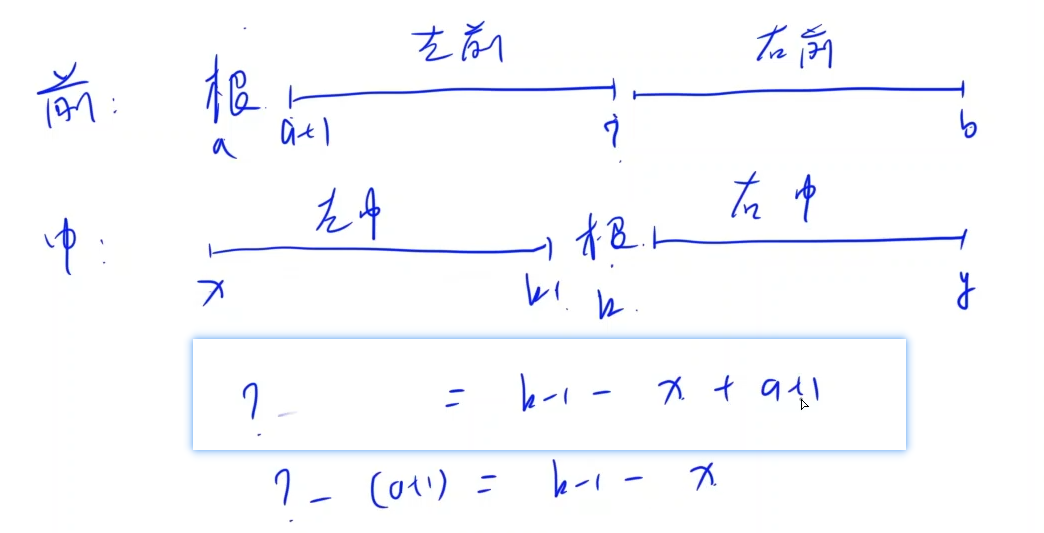
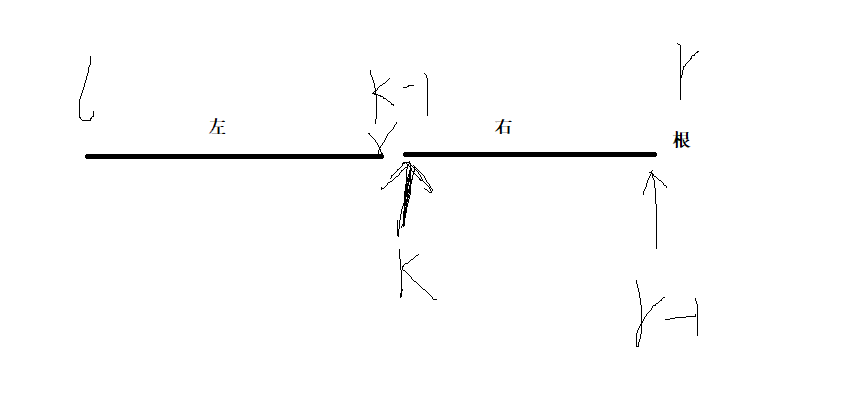
30.46. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
//和那个重建二叉树思路有一点点类似
//画图确定范围
class Solution {
public:
//1.搞一个全局变量
vector<int> seq;
bool verifySequenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
seq = sequence;
return dfs(0, seq.size() - 1);//dfs的是范围
}
//dfs的是范围
bool dfs(int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return true; // 1.如果子序列为空或只有一个节点,它必然是BST的后序遍历结果
int root = seq[r]; // 2.根节点 子序列的最后一个节点是当前子树的根节点
int k = l;//左右子树的分界线(找到右子树的第一个元素)
while (k < r && seq[k] < root) k++; // 找到左子树和右子树的分界点
for (int i = k; i < r; i++)//遍历右子树,如果右子树中,有元素小于根节点就不满足二叉搜索树
if (seq[i] < root)
return false; // 如果在右子树中找到比根节点小的值,则不是合法的BST后序遍历
return dfs(l, k - 1) && dfs(k, r - 1); // 递归检查左子树和右子树
}
};
31.26. 二进制中1的个数
//记住就好, x与-x的与
int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}//可以得到最后一个1
32. 49. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
//最后要改成中序遍历的结果
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode *pre = nullptr , * head = nullptr;
TreeNode* convert(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return nullptr;
dfs(root);
//力扣专著
// leetcode 是 循环链表, 要加上 这里
// 循环链表 首尾相连, pre 最后在 链表尾结点
//head->left = pre, pre->right = head;
return head;
}
void dfs(TreeNode * cur)
{
if(!cur)return ;
dfs(cur->left);
if(!pre)head = cur;//这个头结点是我们要的答案
else
{
//画图
pre->right = cur;
cur->left = pre;
}
//更新前驱节点
pre = cur;
dfs(cur->right);
}
};
34.32. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
维护两个指针,一个从头一个从尾
使得:前指针前面都是奇数,后指针都是偶数
前指针遇到偶数就停下来,遇到奇数就前进
后指针遇到奇数就停下来,遇到偶数就前进
如何前指针的下标和后指针的下标不同,就交换两个数
while(i < j)
{
while()
while()
}
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
int i = 0 ,j =array.size()-1;
while(i < j)
{
while(i<j && array[i] % 2 == 1)i++;
while(i<j && array[j] % 2 == 0)j--;
if(i<j)swap(array[i],array[j]);
}
}
};
35.60. 礼物的最大价值
非常经典的dp问题,太难了,直接pass
36.63. 字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
class Solution {
public:
char firstNotRepeatingChar(string s) {
unordered_map<char , int>hash;
for(auto ch : s)hash[ch]++;
//要求返回第一个只出现一次的字符,我们只能再变量一次字符串,而不是哈希表
for(auto ch : s)
{
if(hash[ch] == 1)return ch;
}
return '#';
}
};
37.85. 不用加减乘除做加法
class Solution {
public:
int add(int num1, int num2){
while(num2)
{
int sum = num1 ^ num2;//不进位
int carray = (num1 & num2)<<1;//进位
num1 = sum , num2 = carray;//把进位拿去加,直到加为0
}
return num1;//num1是答案
}
};
38.47. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//dfs中的条件是难点:没有左右子树,且遍历到这里刚好sum减到了0,才可以把这条路径放进去
class Solution {
public:
//res是最中的答案,path是其中的一条路
vector<vector<int>>res;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(!root)return {};//标准
dfs(root,sum);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode * node , int sum)
{
if(!node)return;//标准
path.push_back(node->val);
if(!node->left && !node->right && sum - node->val == 0)res.push_back(path);//这个是难点
dfs(node->left,sum-node->val);
dfs(node->right,sum-node->val);
path.pop_back();
}
};
39.82. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
编号: 旧 = (新+m)%n
f(n,m) = (f(n-1,m)+m)%n;
class Solution {
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m){
if(n == 1)return 0;
return (lastRemaining(n-1,m)+m)%n;
}
};
40.39. 对称的二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool res = true;
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);//难点是看出来要把左右节点作为参数传给dfs
}
bool dfs(TreeNode * p, TreeNode* q)
{
if(!p || !q)return !p && !q;//这句话也是难点
//上一步p为空或者q为空,都直接返回了,到了这里,p和q肯定都不为空
if(p->val != q->val)return false;
return dfs(p->left,q->right) && dfs(p->right,q->left);
}
};
42.38. 二叉树的镜像
class Solution {
public:
void mirror(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return ;
swap(root->left,root->right);//swap能直接换节点!,这个有点吊
mirror(root->left);
mirror(root->right);
}
};
44.43. 不分行从上往下打印二叉树
//层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return {};
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<int> res;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
//res.push_back(q.);//这里我当时卡住了,不知道怎么把队列的值放进去
auto t = q.front();//1.先拿队列头
q.pop();//2.弹出队头
res.push_back(t->val);
//注意:这里不用for循环,直接就把t的左右子树加进去就行了
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
}
return res;
}
};
45.44. 分行从上往下打印二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//相比较43题,你需要在while循环中嵌套一个while循环
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>>res;
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return {};
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
//分层
int len = q.size();
vector<int> path;//每一层
while(len--)
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
path.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
}
res.push_back(path);
}
return res;
}
};
补充45. 之字形打印二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//相比较43题,你需要在while循环中嵌套一个while循环
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>>res;
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return {};
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
bool flag = false;//表示不用翻转
while(!q.empty())
{
//分层
int len = q.size();
vector<int> path;//每一层
while(len--)
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
path.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
}
if(flag) reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
flag = !flag;
res.push_back(path);
}
return res;
}
};
48.25. 剪绳子
//直接上结论:
//0.如果小于3,就直接返回1*(n-1)
//1.如果这个数%3余1,就先拆分出一个4
//2.如果这个数%3余2,就先拆分出一个2
//3.将这个数拆分成尽可能多的3,最后还剩下多少就再乘多少
class Solution {
public:
int maxProductAfterCutting(int length) {
if(length<=3)return 1*(length-1);//n>=2,m>=2表示绳长大于等于2,且分的段数大于等于2
int n = length;
int sum = 1;
if(n%3 == 1) sum *= 4,n -= 4;
if(n%3 == 2) sum *= 2,n-= 2;
while(n) sum*=3 , n -= 3;
return sum;
}
};
49.88. 树中两个结点的最低公共祖先
//代码很简单,只有一函数即可
//以下情况是一句代码:
//1.如果p和q都属于这颗树,就返回这颗树
//2.如果q属于这颗树,p不属于,就返回q
//3.如果p属于这颗树,q不属于,就返回p
//不管怎么说,都是一句话,if(q==root || q==root)return root;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(!root)return nullptr;
if(p==root || q == root)return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
if(left && right)return root;//一个在左,一个在右,就返回根节点
if(left)return left;//只有左面,就返回左面
else return right;//只有右面,就返回右面
}
};
50.17. 从尾到头打印链表
//小小翻转列表,直接拿些
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
if(!head)return {};
if(!head->next)return{head->val};
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
auto next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
vector<int> res;
//头节点是pre
while(pre)
{
res.push_back(pre->val);
pre = pre->next;
}
return res;
}
};
51.61. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
//双指针
//哈希表
//维护一个i,j区间:
//当我们把一个新的字符加到哈希表中,大于了1时,
//我们就要删掉i,j区间内所有出现1的字符,直到遍历到那个大于1的字符为止,
//此时,我们再计算当前的答案
class Solution {
public:
int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(string s) {
if(s.empty())return 0;
int res = 0;
unordered_map<char ,int> hash;
for(int i = 0 , j = 0 ; j < s.size() ; j ++)// i,j 区间
{
if((++hash[s[j]]) > 1)//开始维护
{
while(hash[s[i]] == 1)
{
hash[s[i]]--;
i++;//过
}
//此时,我们就遍历到那个重复字符
hash[s[i]]--,i++;
}
res = max(res , j-i+1);
}
return res;
}
};
53.20. 用两个栈实现队列
//思路要搞定:
//其中一个栈,有元素进就先进,
//当要弹出元素时,先从一个栈中将元素放到另一个栈中,再弹出
//考查队头,原理同上
//判空:两个队列同时为空才是空
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stk1 ,stk2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stk1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
if(!stk2.empty()){
int t = stk2.top();
stk2.pop();
return t;
}
else
{
while(!stk1.empty()){
stk2.push(stk1.top());
stk1.pop();
}
int t = stk2.top();
stk2.pop();
return t;
}
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
if(!stk2.empty())return stk2.top();
else
{
while(!stk1.empty()){
stk2.push(stk1.top());
stk1.pop();
}
return stk2.top();
}
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
if(stk1.empty() && stk2.empty())return true;
else return false;
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
54.83. 股票的最大利润
//贪心
//先买再卖
//如何枚举
//枚举在某天卖
//开一变量,计算前i天的最小值minV
//如果前天的股票价格>minV,比较一下max(res,当天股票价格-minV)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDiff(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty())return 0;
int minV = nums[0];
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i < nums.size() ;i++)
{
minV = min(minV,nums[i]);//得到前几天股票的最低价
res = max(res , nums[i]-minV);//res与(当前股票价格-前几天股票的最低价)进行比较
}
return res;
}
};
40. 顺时针打印矩阵
//蛇形数组
//走到不能走为止:
//1.越界了不能走
//2.已经走过了不能走(加一个数组标记是否走过)
//每都先计算一下:下一步能不能走,不能走,就换下一个方向
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
if(matrix.empty())return {};
int n = matrix.size() , m = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> res;
vector<vector<bool>>st(n,vector<bool>(m,false));
int dx[4] = {0,1,0,-1} , dy[4] = {1,0,-1,0};//四个方向的向量:右下左上
int x = 0,y = 0 ,step = 0;//起始点,方向
for(int i= 0 ; i < n*m ;i++)
{
res.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
st[x][y] = true;
int a = x + dx[step] , b = y +dy[step];//先计算一下,下一个位置能不能走,不能走就换下一个方向
if(a < 0 || a > n-1 || b <0 || b > m-1 || st[a][b])
{
step = (step + 1)%4;
a = x + dx[step] , b = y +dy[step];
}
x = a ,y =b;
}
return res;
}
};
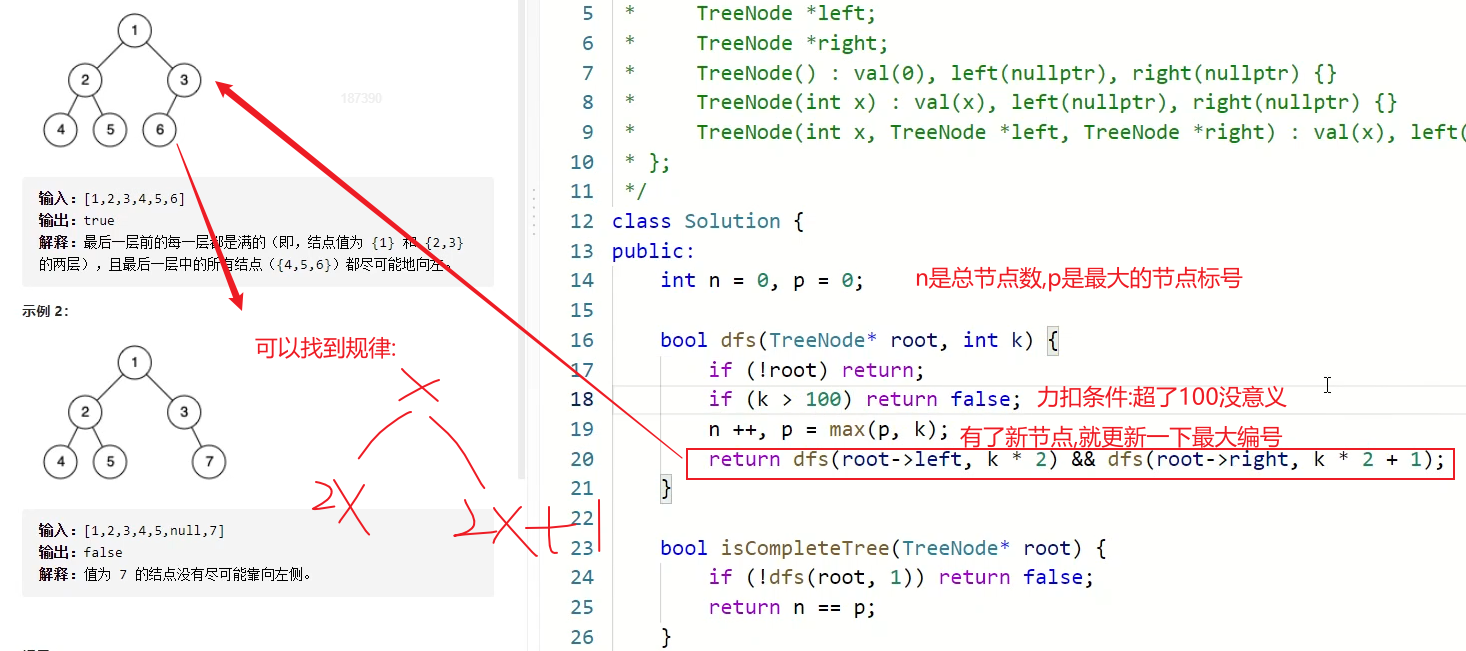
补充:判断一颗树是不是完全二叉树:
LeetCode 958. 二叉树的完全性检验
可以根据编号找规律:
如果是完全二叉树的话:
- (节点的总个数) 一定 是 等于 (最大的节点编号 )
class Solution{
public:
int n = 0 , p = 0;
bool dfs(TreeNode * root, int k)
{
if(!root)return true;
if(k>100)return false;//溢出
n++ , p = max(p,k);
return dfs(root->left,2*k) && dfs(root->right,2*k+1);
}
bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode * root)
{
if(!dfs(root,1))return false;//1表示传进去的是根节点,return false表示节点个数溢出
return n == p;
}
};